What is it?
LIA is a tool based on generative artificial intelligence (AI) that's integrated into the Library's search engine. You can use it to ask questions and obtain answers from sources of academic information. Its name is a combination of the word Library and IA (the acronym for AI in Catalan).
It uses ChatGPT 3.5 technology to identify the five most relevant resources in the Library's search engine results, and generates a response based on the title and abstract.
The AI assistant's features:
You'll find the AI assistant in the Library's search engine. Click on the Ask LIA button in the sidebar to open the assistant so that you can enter your question.

Rate your experience and share your thoughts on the AI search assistant using this feedback form.
The assistant will get better the more it's used. Like any other generative AI tool, we recommend that you always check the information to ensure the answers are accurate, and to avoid any possible errors or biases.
The answers it gives may contain errors, as can happen with any generative artificial intelligence tool. For this reason, it is important to always check each answer against the original sources to make sure that it is complete and correct.
How did we get here? The LIA search assistant has been launched after a pilot test involving the participation of the entire UOC Community.
Bear in mind:
- Currently, the tool generates answers based on the abstracts available in the search engine.
You can access the full text of the sources proposed by the assistant when they are open access or subscribed to by the Library.
- It can't interpret some advanced search requests, such as searching for information in a specific language (e.g. "only search for resources in English").
- Each question is self-contained and unrelated to previous questions. For example, if you ask: "What subjects did Simone de Beauvoir write about?", you cannot then ask: "Can you give me some examples?" You must phrase the questions like this: "What is The Second Sex by Simone de Beauvoir about?"
- LIA has a daily limit of 100 queries per person and 10,000 queries in total for the whole UOC community.
How do I use the assistant?
Ask a question
Your questions should relate to academic or scientific matters and be as clear and detailed as possible. Make the query as specific as you can, and word it as a question. If you need more help, take a look at these guidelines on prompts for generative AI tools.
Here are a few examples of questions you could ask:
Did Picasso's time in Paris influence his artistic style?
How can diversity in clinical trials be improved?
You can carry out searches in Catalan, English and Spanish. However, as most academic content is in English, if you ask a question in another language, the assistant will search sources in both English and the other language.
The answers
For example, if you ask "What sections should a good marketing plan have?", you'll get:

-
Overview
A brief answer in the language of the search, with a list of the sources used.
-
Assessment
Use the thumbs up or thumbs down icon to rate the answers.
-
Try again
There may be more than one possible answer and a variety of relevant resources. If you're not satisfied with the answer, you can click on the button.
-
Sources
You can access the full text of the sources proposed by the assistant when they are open access or subscribed to by the Library.
-
View more results
A direct link to the UOC Library's search engine with more results on the subject.
-
Related research questions
Recommended questions in case you wish to expand your search.
-
Apply filters
Choose the type of document (peer-reviewed articles, articles, books, etc.) or when they were published to filter the sources used by the tool to answer your question.
Development of the project

Ball State University,
Cardiff University,
Free University of Bozen-Bolzano,
Keio University,
Sorbonne University,
Swansea University,
Swiss Library Service Platform (SLSP),
The New School
Tulane University,
University at Buffalo (SUNY),
University College London (UCL),
University of Liège,
University of New South Wales (UNSW),
Waseda University,
Yale University,
Beijing Normal University
Universitat Oberta de Catalunya (UOC)
Our aims
We're looking for innovative solutions to offer the best possible service. Integrating AI in the search engine is a starting point to improve the user's search experience, guiding them and making it easier and more intuitive.
Operative group:
Rosa Llussà, member of the Research Assistant working group
Our priority is to make it easier and easier to find what you need, and this pilot test is a step in that direction. We'll evaluate the tool to find out if it meets the needs of the UOC community.
Operative group:
Sara Zerini, member of the Research Assistant working group
Generative AIs using natural language questions aid the information retrieval processes and help explore the literature from any domain of knowledge.
Operative group:
Joaquim Espín, member of the Research Assistant working group
The pilot test will be carried out in three stages:
Internal testing by a Library and Learning Resources department working group.
Configuration and initial customization of the tool.
First joint assessments by the eighteen participating institutions, based on 500 tests:
- General structure and length of results: Changes proposed to make the answers more complete and improve their structure.
- Sources of information: DataCite records are temporarily excluded. The sources the tool uses need to be accurately identified.
- Limitations: The instructions that it does not currently recognize need to be made clear.
The pilot test is extended to the entire Library and Learning Resources department and to UOC teaching staff, research staff and administrative staff.
The pilot test is opened up to the entire UOC community.
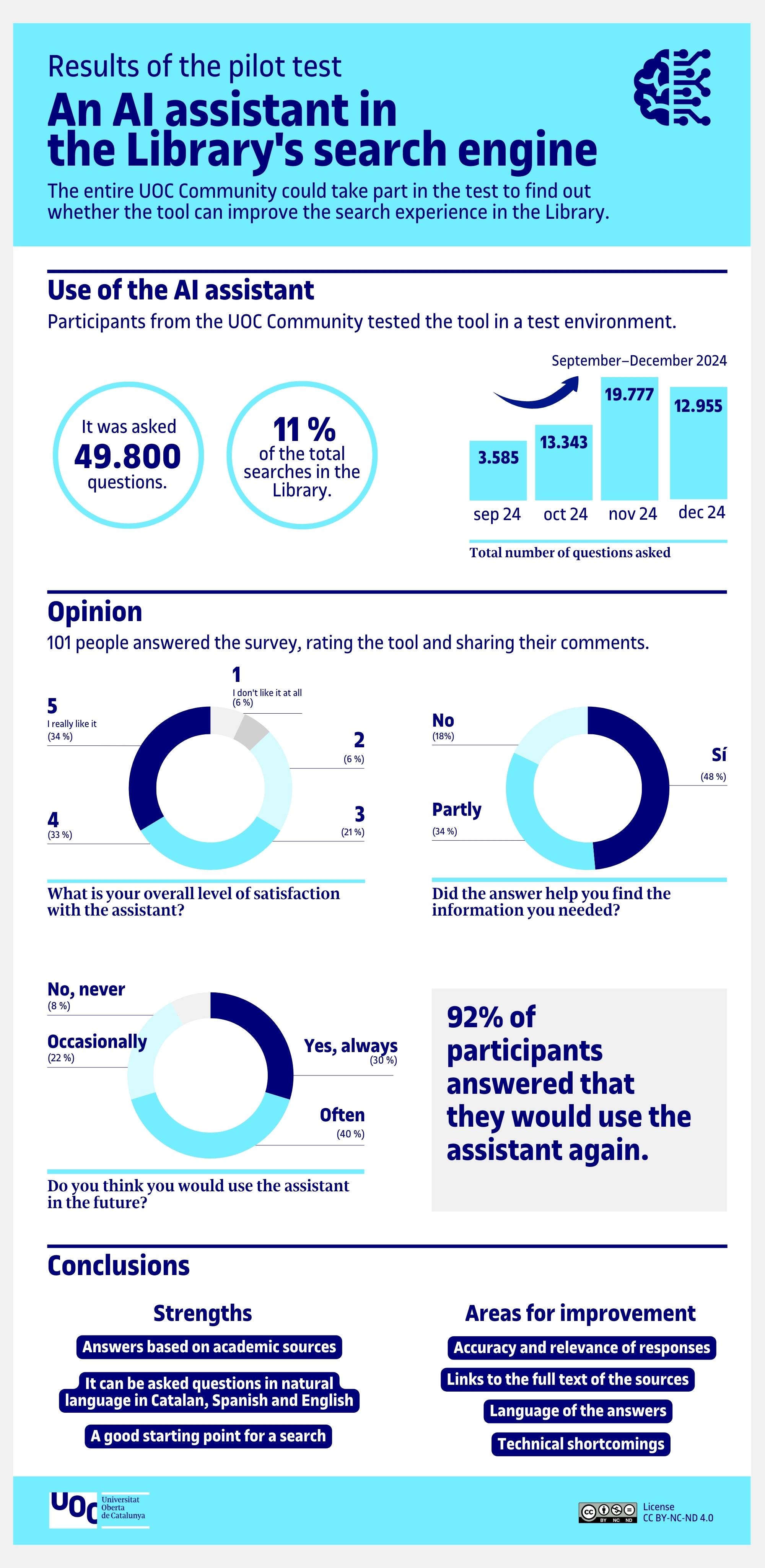
The AI assistant was asked nearly 50,000 questions, and 101 users shared their comments and ratings. Some 92% said that they would use the tool again for their searches.
Some areas for improvement were also identified:
- Increased accuracy and relevance of the answers, and fewer context errors.
- Inclusion of advanced features, such as filters by document type, voice assistants and machine translation.
- Consistent use of language, and an intuitive and customizable interface.
The Library team is in contact with the developers of the AI assistant to propose possible improvements to the tool.
Click the image to open the infographic.
With the AI search assistant integrated into the Library's search engine, some of the limitations identified during the pilot test can be overcome, including the ability to filter by document type or time period.