This Library guide covers the tools at your disposal to manage your research data.

Research data management
The importance of data management in the scope of research has increased in recent years along with the ability to disseminate and share data with other researchers and the general public.
Research data management at the UOC
Research data management (RDM) encompasses the organization, structure, storage and processing of the data used or generated during a research project.
The RDM is present in all research phases:
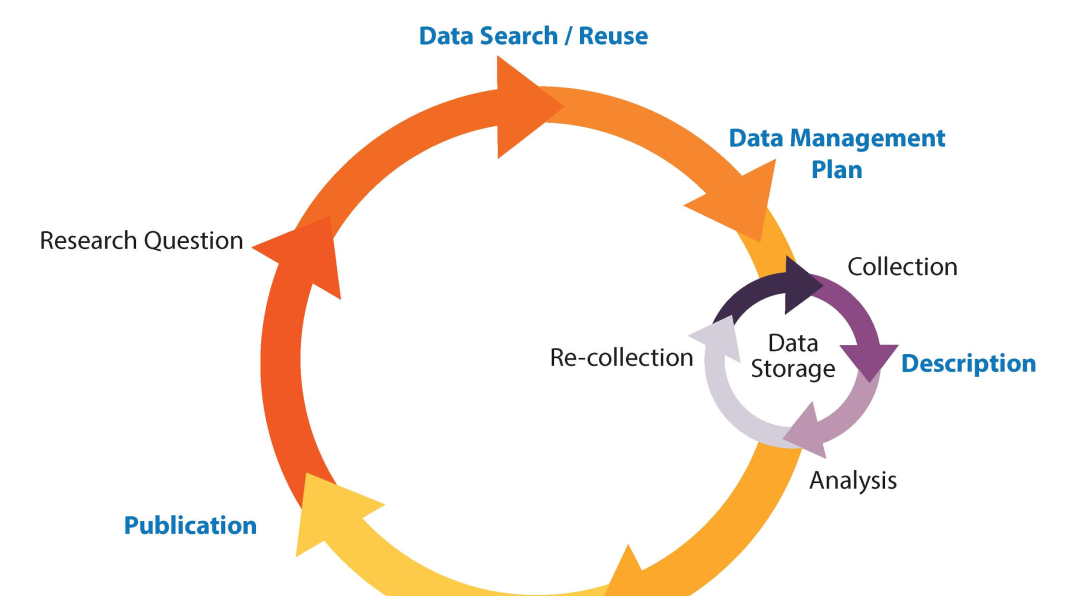
- Data creation and planning their reuse
- Processing and organization: structuring and metadata
- Analysis
- Preservation: security, access, storage and retrieval
- Share: publish and be cited
- Reuse
The Research Data Management Plan
What is a Data Management Plan (DMP)?
A Data Management Plan (DMP) is a formal document that describes the data life cycle both during a research project and when it has been completed.
The DMP's objective is to consider aspects such as the methodology and standards to be used for data management and how they will be shared, curated and preserved in the future.
The data management plan is not a fixed document, but evolves during the lifespan of the research project.
How is a DMP produced?
Template to create a data management plan in accordance with the requirements of the H2020 programme:
This document was prepared by the CSUC's Working Group to Support Research.
What are the legal aspects concerning data protection?
The protection of personal data includes the protection of people's basic rights and freedoms applied to an R&D&I project, and their protection against possible use by unauthorized third parties.
What are the ethical aspects concerning data protection?
Ethical aspects concern the data that can be shown, the time spent and the anonymity of the people involved, respecting dignity and integrity in order to guarantee privacy and confidentiality.
Resources and related documentation:
Under which licence can you publish your data?
The document Guidelines on Open Access to Scientific Publications and Research Data in Horizon 2020 states:
"As far as possible, projects must then take measures to enable third parties to access, mine, exploit, reproduce and disseminate (free of charge for any user) this research data. One straightforward and effective way of doing this is to attach Creative Commons Licence (CC-BY or CC0 tool) to the data deposited."
Further information can be found at:
How are data cited?
DataCite establishes that data must be cited in the same way that we cite other bibliographic information sources, such as articles or books.
Citing research data will enable you to:
- Easily reuse and verify the data.
- Monitor the potential impact of the data.
- Create an academic structure that acknowledges and rewards the data producers.
Structure templates:
- Creator (Year of publication): Title. Publisher. Identifier.
- Creator (Year of publication): Title. Version. Publisher [Type of resource]. Identifier.
Note: The identifier refers to the permanent DOI, handle or URL (preferably linkable).
Further information can be found at:
Where are research data published?
Open data journals
The last few years have seen a growing interest in publishing research data in open access in order to support research's transparency, visibility and impact, as well to guarantee that the data can be freely accessed, preserved, used and reproduced.
This is the context that has spawned data journals. There are two types of data journal, allowing authors to publish their articles in two different ways:
- Publishing data as a data paper: these journals only publish data in data paper format. This is a new publishing format based on datasets.
- Publishing data along with an article (enriched or enhanced publication): these journals present data and articles side-by-side. Usually, this type of journal doesn't collect complete data, but instead provides links within the articles to specific data repositories where you can find the data.
Authors are required to send their datasets to the data repositories included on its list, which are organized by discipline and recognized by the corresponding community.
It provides authors with use of the Dataverse open access repository.

Have a look at the following compilation of data journals according to their subject area, access type and scientific impact in the leading international indexes.
You can also look at the comparative chart for open access data produced by the library of the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona and the list of repositories maintained by the Erasmus University Library.
Repositories
- In the CORA research data repository. The aim of this repository is to publish the research data produced by all members of the UOC community. To publish your research data in this repository, contact the research data management service.
- In a thematic repository. Find the most suitable one in: Re3data, the Registry of Research Data Repositories.
- In other multidisciplinary repositories. Take a look at the table comparing repositories produced by the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona's Library.
What are research data?
According to the European Commission (EC), research data refer to information, in particular facts or numbers, collected to be examined and considered as a basis for reasoning, discussion or calculation. Data include statistics, results of experiments, measurements, observations resulting from fieldwork, survey outcomes, interview recordings and images.
A fake story in a trustworthy guide to the FAIR principles for research data.
Types of research data
- Observational: data captured in real time. For instance, neuroimages, sample data, sensor data, questionnaire data
- Experimental: data captured on laboratory equipment. For instance, gene sequences, chromatograms, magnetic field data
- Simulation: data generated based on test models. For example, climatological, mathematical or economic models
- Derived or compiled: difficult-to-reproduce data. For instance, text and data mining, 3D models or compiled databases
- Reference: data conglomerate or dataset. For instance, databases of gene sequences, chemical structures or spatial data portals
Benefits of managing and sharing data
- Validation of the results obtained.
- Data localization and comprehension.
- Reduces the duplication of data collection and the costs involved.
- Complies with the requisites of calls for research.
- Promotes scientific debate.
- Promotes innovation and new potential uses of the data.
- Encourages collaboration between data users and creators.
- Increases research impact and visibility.
- Increases your reputation when other people cite your work.
Who owns the data?
According to Article 12 of the Law on Intellectual Property:
The databases “that by selection or arrangement of their content constitute intellectual creations” are protected by copyright.
However, the raw data included in a database have no authorship and, therefore, are not intellectual property.
Funding bodies and research data
H2020
The European Commission requires all projects receiving H2020 funding to produce a data management plan (DMP) and to share the data as openly as possible. Likewise, the data must be FAIR: findable, accessible, interoperable and reusable.
More information:
For activities receiving European Research Council (ERC) funding, consult: Guidelines on Implementation of Open Access to Scientific Publications and Research Data in Projects Supported by the European Research Council under Horizon 2020
Spanish National Plan 2017-2020
With the aim of promoting access to research data from projects receiving public funding, the Spanish National Scientific and Technical Research and Innovation Plan mentions optionally including:
A data management plan that must be deposited in a national or international repository once the project has been completed and the necessary time passed as established by the funding programme, while taking into account those situations where the data must protected for reasons of confidentiality, security or data protection, or where necessary for the commercial exploitation of the results obtained.


